
HOME
WEDDING
CUSTOMS
ANATOLIAN (TURKISH) SOCIAL
RITUALS, INCLUDING MARRIAGE

Zawaj.com Editor's Note: This article, taken from the Turkish Odyssey website, was written from a pro-Western viewpoint. Zawaj.com did not write this article, but we did edit it somewhat to remove the more blatant anti-Islamic references. We're just supplying it for the sake of information. You should use your own judgement.
Families are divided into several types according to social, economic and local conditions. The traditional extended and nuclear families are the two common types of families in Turkey. The traditional extended family, generally means that three generations live together: grandfather, adult sons and sons' sons, their wives and their unmarried daughters a married daughter becomes a member of her husband's family and lives there. There is a unity of production and consumption together with common property. This type of family is becoming more and more rare today. The nuclear family, parallel to industrialization and urbanization, replaces traditional families. There are some economic, traditional and emotional conditions that form the duties and responsibilities of the modern nuclear family member. As for the economic conditions, each individual is supposed to play a part in supporting the continuation of the family. The father is usually responsible for making the basic income, the mother may perhaps contribute by working and if not, will assume full-time take care of the home. Grandparents may also supply help with incomes from their pension or returns from owned property and rents. Younger children help with the housework (re-pairing, painting, cleaning) and when older contribute by usually covering at least their own expenses. Tradition places the father as the head of the family, but the mother has equal rights. The father is the representative and protector of the family whereas the mother takes care of all the day to day things.
WOMEN
|
|
As Turkey is a Muslim country, Islam plays an important role in the lives of women. When Islam made marriage laws and put a limit on the number of wives allowed, it was accepted as the first system to give some economic rights to women by saving them from the sole sovereignty of their husbands.
In Turkey, following the collapse of the Khilafat and the declaration of the Republic in 1923, Ataturk embarked on a program of Westernization and secularization, along with fanatical attempts to abolish Islamic customs from Turkish society. Unfortunately, this program continues today.
In 1926, a new code of Turkish civil law was adopted which suddenly changed the family structure. Polygamy was abolished along with religious marriages. A minimum age for marriage was fixed at 15 for girls and 17 for boys. The right to vote for women was granted at the municipal level in 1930 and nationwide in 1934.

|
The charter of the International Labor Organization adopted in 1951, declaring equal wages for both sexes for equal work was ratified by Turkey in 1966.
Still today, the husband is the head of the family. A woman does the housework, and if a woman needs to work outside the home she has to get the approval of her husband. As a Turkish proverb says "a husband should know how to bring food and the wife to make it suffice" confirming once again a woman's place in the home.
Women today
Social life consists of two different places: Inside and outside the home. Women leave the outside world to the men, generally remaining in the home. Women get married at an earlier age than men and settle into their role of housewife and home maker. As the education level of women increases, the fertility rate decreases. Nearly every female university graduate has only one child.
9 million of the 21 million working population of Turkey are women. In the rural areas, the rate of working women, especially in agriculture, is very high. However, women work in this sector as an extension of their housework and not to make a living. In urban areas, women hold important posts in both public and private sectors, the arts and sciences. Today, Turkish women are bank managers, doctors, lawyers, judges, journalists, pilots, diplomats, police officers, army officers or prime ministers.
Nearly two thirds of health personnel including doctors and pharmacists, one quarter of all lawyers and one third of banking personnel are women.
As for the politics, in the elections of 1937, the number of woman MP's was 18, which meant 4.5%. Today, unfortunately, this rate is much less than before. However, Turkey has also seen Tansu Ciller as the first woman Prime Minister.
A new law proposition
A package called "Democratization of the family" is a new law preposition awaiting parliamentary discussion and enactment and it will include changes in the position of women, some of which are as follows:
- The cancellation of former obligatory permission from their husbands for women to work.
- Equality in the case of adultery.
- In the case of divorce, equality in the sharing of belongings which were acquired after marriage.
MARRIAGE

|
In the traditional family, marriage is still a family rather than a personal affair. Marriages are not conducted by the Imam anymore as they were before the Republic. By law they have to be civil. Approximately 40% of marriages are only civil, 50% are both civil and religious, 10% are only religious which means they are not legal. Polygamy is very rare and only in some villages with a rate of 3%. It is legally forbidden to marry before the age of 15 for women and 17 for men. The average age for girls to marry is around 17-18. Early marriages are more frequent in rural areas. For young men in big cities the problems of receiving an education, military service and acquiring a job are among the reasons that delay marriage.
BIRTH
The continuity of a family is provided by children. With the development of people's educational levels, the belief in the continuity only being provided by sons is losing its effect. At the pregnancy of a new bride, an excitement among family members grows. Upon hearing the good news, a golden bracelet comes immediately as a present from the mother-in-law. In rural areas a pregnant woman declares it with some symbols mostly on her clothing; her scarf, motifs on it and suchlike.
For the births, in rural places midwives are present, whereas in big cities hospitals are common. After the birth, the new mother receives presents of gold and the child gets all manner of gifts. The mother is not supposed to go out from her house for 40 days. If she works, she has a holiday of 40 days automatically. Relatives, friends and neighbors are all helpful. In the first three days only close relatives come to visit, but in the following days the others also come to visit with lots of presents. Breast-feeding continues normally until the age of two or even later and then weaning is sudden.
In Anatolia there is a custom of planting trees in the names of newly born children. Chestnut, mulberry and apple trees are planted for girls, poplar or pine trees for boys. Planting trees for boys is a kind of investment for him to be used in his marriage when he grows up.
Naming a child
Turkish names always have meanings. Some of the children's names may derive from the time in which he was born; Bayram (Feast), Safak (Dawn), Bahar (Spring), Ramazan (the holy month, Ramadan), or the events during the birth; Yagmur (Rain), Tufan (Storm), or express the parents' feeling about the child, if they want him to be the last one; Yeter (Enough), Songul (Last rose) and sometimes names of elder people in families are chosen as displays of respect.
When a name is selected, it is given by an Imam or an elder person in the family by holding the child in the direction of Mecca (Qible) and reading from the Qur'an into his left ear and repeating his name three times into his right ear.
SUNNET (CIRCUMCISION)

|
Circumcision is an operation in which the foreskin of the penis is removed. It is a practice of great religious significance. Circumcision is known to have been practiced in ancient Egypt even before it was introduced to the Jews as part of Allah's covenant with Abraham. In Islam, however, the authority for circumcision came not from the Qur'an but from the example of the Prophet Mohammed. In Islam, whatever the prophet does or says is called sunnet; therefore this word stands for circumcision in modern Turkish.
Urologists claim that circumcised males have far fewer urinary tract infections and are less at risk for catching sexually transmitted diseases than are uncircumcised males.
As an Islamic country, in Turkey all Moslem boys are circumcised between the ages 2-14 by licensed circumcising surgeons. From the social point of view, the most prominent feature of circumcision is the introduction of a child to his religious society as a new member. This explains the reason for circumcision of people who convert into Moslems as a first step. It is impressed on a boy at a very early age that circumcision is a step for transition to manhood. As long as they are accepted as very important events in people's lives, circumcisions are generally made with big ceremonies in festive atmosphere.
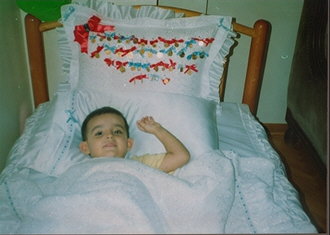
|
If a family has more than one boy, they wait for an appropriate time to perform it altogether. In this case the younger child might be less than 4. In some rural areas, villagers sometimes share expenses of a circumcision feast like they do with the work. Wealthy people may take poor boys or orphans together with their children for circumcision. Charity organizations make collective ceremonies for poor boys and orphans. Considering school periods of children, circumcisions are held in summer months while the children are on vacation, from June through September at weekends.
Circumcision Ceremony
When a family determines a date for their feast, they invite relatives, friends and neighbors by sending invitation cards in advance. Depending on the economic position of families, feasts might take place in a ceremonial hall or a hotel instead of a house. They prepare a highly decorated room for the boy with a nice bed and many colorful decorative things. Boys should also wear special costumes for this feast; a suit, a cape, a scepter and a special hat with "Masallah", meaning "Allah preserve him", written on it.
In the morning of the feast, the children of guests are all taken for a tour around in a big convoy with the boy either on horseback, horse carts, or automobiles. This convoy is also followed by musicians playing the drums and the clarinet.
After they come back, the boy wears a loose long white dress and, is circumcised by the surgeon while somebody holds him. This person who holds is called kirve, and has to be somebody close to the boy. In the eastern parts of Anatolia, this is the first contact of a big relationship which will continue for lifetime. He will play an active role in the boy's lifetime and have nearly equal rights with the father in decisions. Although there is no blood relation to his kirve, the boy will not even be allowed to marry his kirve's daughter in order not to have incest because he is considered to have become somebody from the family.
After the circumcision, the boy is in pain and has to be kept busy with music, lots of jokes or some other animation. Presents also are given at this time to help him forget his pains. In the meantime words from the Qur'an are recited and guests are taken to tables for the feast meal which is a special one laid with different food changing from region to region. After a few days the boy recovers and festivities end.
Today, there is a small group of people who prefer their children to be circumcised in hospitals while they are in hospital after birth, whereby ignoring the traditional side.
DIVORCE
Divorce is not very common. Even if a couple is unhappy, they usually continue their lives for their children's sake or not to suffer from the social pressure it may evoke. The other reason is economic. If a woman does not work, she does not have many alternatives when divorced. After a certain age, in a country where employment is a problem, it is really a risk to survive.
From the legal point of view, when couples divorce, each of them gets his own belongings without taking the things obtained together into consideration. A new law proposal is waiting to be enacted in parliament. The change will allow the sharing of everything equally.
DEATH AND BURIAL
Throughout the ages in Anatolia, many different rituals regarding death and burial have been applied. Types of graves have differed. Graves under the floors of houses, wooden rooms, tumuli, chamber-like graves, rock-tombs, sarcophagi, domed or conical tombs (turbe, kumbet) and mausoleums are some places where the dead have been laid. Although it is difficult, death is considered to be as a natural part or aspect of life. There are many people who prepare themselves for death by putting necessary amount of money for funerals in their bank accounts, keeping winding sheets ready, or buying land in a cemetery in advance. Dying as martyrs is an honorable thing. In Islam, it is believed that martyrs go directly to heaven.
When somebody dies, the body is laid on a bed in a separate room, the head facing the direction of Mecca, eyelids closed, the big toes are tied to each other and the two arms rest on both sides next to the body. Burial has to take place as soon as possible during the daytime. If somebody dies in the late afternoon, he is buried the next day. The corpse might rest for a period of time in a cool place or a mortuary but only if there are close relatives coming from a far away place.
According to religious belief, the body should be properly washed and given ablution. Therefore, dead people have to be washed by authorized people, and always women by a woman, men by a man. Meanwhile the death is declared from a mosque minaret by a muezzin with some words from the Qur'an together with his name, funeral time and place. After the ablution the body is dressed in a white shroud, put in a wooden coffin covered with a green piece of cloth. A martyr's coffin is covered with the Turkish flag. The coffin is carried to the table outside in the courtyard of a mosque on people's shoulders before prayers. Nobody stands in front of the funeral procession and people in the street stand up and salute the funeral motionless and in silence.
While the coffin rests guarded on the table outside, people perform their regular prayers. From within the mosque, following the prayers, they all come out and line up in front of the coffin to take part in the funeral service under the leadership of the Imam. Women are not allowed to join this service. At the end of the service, the Imam asks people what they thought of the deceased and answers are always positive: "He was good. May Allah bless him. Mercy be upon his soul, etc." Funeral services are not held for parricides or the stillborn.
Interment
The coffin is carried to the cemetery by a hearse followed by a long convoy. Graves are rectangular in shape and designed to accommodate only one person. The deceased is buried in only the shroud not the coffin. The body is laid on its right shoulder facing the direction of Mecca. The tombstone is on the head's side.
The Imam's prayers signify the end of the burial. The deceased is commemorated on the seventh and fifty-second days of his death with Islamic readings; mevlit. Sometimes big funerary meals or halvah are offered to the poor and surrounding people.
A FEW PROVERBS
Oral tradition continues with proverbs. When considering daily life, proverbs embody the deepest feelings and beliefs of the Turkish people. They reveal a nation's character in its finest details. Following is a selection of some proverbs from among thousands:
- If Allah wants to make a poor man happy he first makes him lose his donkey and then allows him to find it again.
- He who handles honey has the chance to lick his fingers.
- When a bald man dies, everybody remembers "what golden hair he had"; when a blind man dies, they say "what beautiful eyes he had".
- Two tightrope walkers cannot perform on the same tightrope.
- A vinegar seller with a smiling face makes more money than a honey seller with a sour face.
- The hunter is sometimes hunted.
- Stretch your legs to the length of your blanket. (Know your limits)
- Water priority to the youngsters, talking priority to the elders.
- You reap whatever you sow.
- A pen is sharper than a sword.
- A tree is bent while yet it is young.
- There is nothing more expensive than what is bought cheaply and there is nothing cheaper than what is bought dearly.
 BACK
TO WEDDING CUSTOMS
BACK
TO WEDDING CUSTOMS

